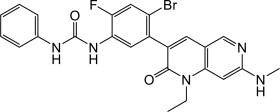
Qinlock
What is Qinlock (Ripretinib)?
Approved To Treat
Top Local Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: This is a prospective, single-center, observational study to explore the correlation between ripretinib exposure and the efficacy and safety in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors
Summary: The goal of this prospective, observational study INTEREST is to collect real-world data on ripretinib treatment in a broad patient population in Germany. Ripretinib will be administered according to the current SmPC. Thus, INTEREST will evaluate for the first time ripretinib in GIST patients in a real-world setting in Germany. The main questions the study aims to answer are: * Evaluate quality of...
Summary: This study is a multicenter, prospective, randomized controlled Phase II clinical trial. The primary endpoint is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of regorafenib combined with envafolimab compared to previously effective maintenance regimens in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors harboring KIT exon 17 mutations who have failed standard treatments.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- QINLOCK 100 mg orally once daily.
- If less than 4 hours have passed since the missed scheduled dose, advise the patient to take the missed dose as soon as possible and then take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time.
- If more than 4 hours have passed since the missed scheduled dose, advise the patient to skip the missed dose and then take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time. [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
- Palmar-Plantar Erythrodysesthesia Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- New Primary Cutaneous Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Cardiac Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Photosensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
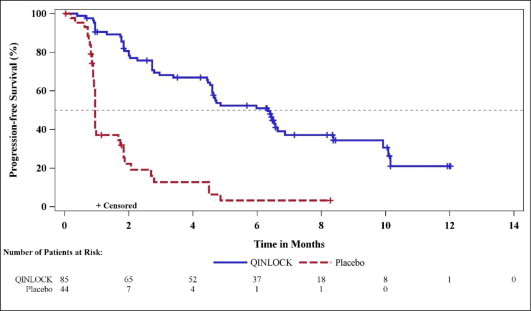
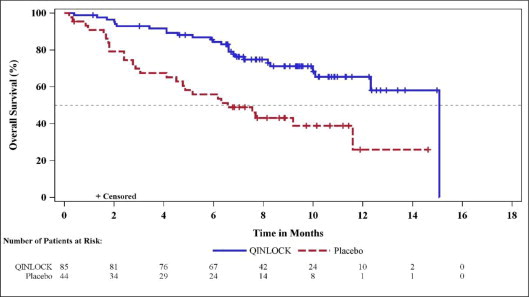
- 90-count bottles NDC 73207-101-30