Brand Name
Spevigo
Generic Name
Spesolimab-Sbzo
View Brand Information FDA approval date: September 01, 2022
Classification: Interleukin-36 Receptor Antagonist
Form: Injection
What is Spevigo (Spesolimab-Sbzo)?
SPEVIGO is indicated for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg. SPEVIGO is an interleukin-36 receptor antagonist indicated for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg.
Approved To Treat
Top Local Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
SPEVIGO (spesolimab-sbzo)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SPEVIGO is indicated for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg.
2DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1Testing and Procedures Prior to Treatment Initiation
Evaluate patients for active or latent tuberculosis (TB) infection. SPEVIGO initiation is not recommended in patients with active TB infection. Consider initiating treatment of latent TB prior to initiation of SPEVIGO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Complete all age-appropriate vaccinations according to current immunization guidelines prior to initiating SPEVIGO for treatment of GPP [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
2.2Important Administration Information
2.3Recommended Subcutaneous Dosage for Treatment of GPP When Not Experiencing a Flare
The recommended dosage of SPEVIGO for treatment of GPP when not experiencing a flare in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg is a loading dose of 600 mg (four 150 mg injections) followed by 300 mg (two 150 mg injections) administered subcutaneously 4 weeks later and every 4 weeks thereafter.
2.4Recommended Intravenous Dosage for Treatment of GPP Flare
The recommended dosage of SPEVIGO for treatment of GPP flare in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg is a single 900 mg dose administered by intravenous infusion over 90 minutes.
If GPP flare symptoms persist, an additional intravenous 900 mg dose (over 90 minutes) may be administered one week after the initial dose.
2.5Preparation and Administration Instructions
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration, whenever solution and container permits. SPEVIGO is a colorless to slightly brownish-yellow, clear to slightly opalescent solution. Do not use if the solution is cloudy, discolored, or contains large or colored particulates.
3DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
SPEVIGO is a colorless to slightly brownish-yellow, clear to slightly opalescent solution available as:
4CONTRAINDICATIONS
SPEVIGO is contraindicated in patients with severe or life-threatening hypersensitivity to spesolimab-sbzo or to any of the excipients in SPEVIGO. Reported hypersensitivity reactions have included drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1Infections
SPEVIGO may increase the risk of infections. During the one-week placebo-controlled period in the Effisayil-1 trial, infections were reported in 14% of subjects treated with SPEVIGO compared with 6% of subjects treated with placebo [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In patients with a chronic infection or a history of recurrent infection, consider the potential risks and expected clinical benefits of treatment prior to prescribing SPEVIGO. Treatment with SPEVIGO is not recommended in patients with any clinically important active infection until the infection resolves or is adequately treated. Instruct patients to seek medical advice if signs or symptoms of clinically important infection occur during or after treatment with SPEVIGO. If a patient develops a clinically important active infection, discontinue SPEVIGO therapy until the infection resolves or is adequately treated.
5.2Risk of Tuberculosis
Evaluate patients for tuberculosis (TB) infection prior to initiating treatment with SPEVIGO. Avoid use of SPEVIGO in patients with active TB infection.
Consider initiating anti-TB therapy prior to initiating SPEVIGO in patients with latent TB or a history of TB in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of active TB during and after SPEVIGO treatment.
5.3Hypersensitivity and Infusion-Related Reactions
SPEVIGO-associated hypersensitivity reactions may include immediate reactions such as anaphylaxis and delayed reactions such as drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) has been reported in clinical trials with SPEVIGO in subjects with GPP [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
If a patient develops signs of anaphylaxis or other serious hypersensitivity, discontinue SPEVIGO immediately and initiate appropriate treatment. SPEVIGO is contraindicated in patients with severe or life-threatening hypersensitivity to spesolimab-sbzo or to any of the excipients in SPEVIGO [see Contraindications (4)].
If a patient develops mild or moderate hypersensitivity during an intravenous infusion or other infusion-related reactions, stop SPEVIGO infusion and consider appropriate medical therapy (e.g., systemic antihistamines and/or corticosteroids). Upon resolution of the reaction, the infusion may be restarted at a slower infusion rate with gradual increase to complete the infusion.
5.4Vaccinations
Prior to initiating SPEVIGO for treatment of GPP, complete all age-appropriate vaccinations according to current immunization guidelines.
Avoid use of live vaccines in patients during and for at least 16 weeks after treatment with SPEVIGO. No specific studies have been conducted in SPEVIGO-treated patients who have recently received live viral or live bacterial vaccines.
6ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypersensitivity and Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
7USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
7.1Pregnancy
7.2Lactation
7.3Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SPEVIGO for the treatment of GPP have been established in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg. Use of SPEVIGO for this indication is supported by data from a randomized, placebo-controlled study which included 6 pediatric subjects 14 to 17 years of age with a history of GPP treated with subcutaneous SPEVIGO (Study Effisayil-2) and evidence from an adequate and well-controlled study of intravenous SPEVIGO in adults with GPP (Study Effisayil-1), with additional pharmacokinetic analyses showing similar drug exposure levels in adults and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older and weighing 40 kg or more [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14)].
The safety and effectiveness of SPEVIGO in pediatric patients younger than 12 years of age or in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg have not been established.
7.4Geriatric Use
There were 2 (6%) intravenous SPEVIGO-treated subjects 65 to 74 years of age and no subjects 75 years of age or older in Study Effisayil-1. There were 6 (7%) subcutaneous SPEVIGO-treated subjects 65 to 74 years of age and 1 (1%) subject 75 years of age in Study Effisayil-2. Clinical studies of SPEVIGO did not include sufficient numbers of subjects 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult subjects.
8DESCRIPTION
Spesolimab-sbzo, an interleukin-36 receptor antagonist, is a humanized monoclonal IgG1 antibody (mAb) against human IL-36R produced in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells by recombinant DNA technology. Spesolimab-sbzo has a molecular weight of approximately 146 kDa.
SPEVIGO (spesolimab-sbzo) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to slightly brownish-yellow, clear to slightly opalescent solution supplied in a single-dose prefilled syringe for subcutaneous use. Each 1 mL prefilled syringe contains 150 mg spesolimab-sbzo, arginine hydrochloride (5.3 mg), glacial acetic acid (0.32 mg), polysorbate 20 (0.40 mg), sodium acetate (3.25 mg), sucrose (51.4 mg), and Water for Injection, USP with a pH of 5.2 – 5.8.
SPEVIGO (spesolimab-sbzo) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to slightly brownish-yellow, clear to slightly opalescent solution supplied in a single-dose vial for intravenous use. Each 7.5 mL vial contains 450 mg spesolimab-sbzo, arginine hydrochloride (39.5 mg), glacial acetic acid (2.4 mg), polysorbate 20 (3.0 mg), sodium acetate (24.5 mg), sucrose (386 mg), and Water for Injection, USP with a pH of 5.0-6.0.
9CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
9.1Mechanism of Action
Spesolimab-sbzo is a humanized monoclonal immunoglobulin G1 antibody that inhibits interleukin-36 (IL-36) signaling by specifically binding to the IL36R. Binding of spesolimab-sbzo to IL36R prevents the subsequent activation of IL36R by its ligands (IL-36 α, β and γ) and downstream activation of pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic pathways. The precise mechanism linking reduced IL36R activity and the treatment of flares of GPP is unclear.
9.2Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of SPEVIGO in the treatment of patients with GPP have not been fully characterized.
9.3Pharmacokinetics
A population pharmacokinetic model was developed based on data collected from healthy subjects, patients with GPP, and patients with other diseases. After a single intravenous dose of 900 mg of SPEVIGO, the population PK model-estimated AUC0-∞ (95% CI) and Cmax (95% CI) in a typical anti-drug antibody (ADA)-negative patient with GPP were 4750 (4510, 4970) mcg∙day/mL and 238 (218, 256) mcg/mL, respectively. After subcutaneous SPEVIGO 600 mg LD followed by 300 mg every 4 weeks, the mean steady-state trough concentration ranged from 33.4 mcg/mL to 42.3 mcg/mL.
When administered intravenously, spesolimab-sbzo AUC increased dose-proportionally from 0.3 to 20 mg/kg, and CL and terminal half-life were independent of dose. Following subcutaneous single dose administration, spesolimab-sbzo exposure increased slightly more than dose-proportionally across the dose range of 150 mg to 600 mg due to increased bioavailability at higher doses.
9.4Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of spesolimab-sbzo or of other spesolimab products.
In subjects with GPP treated with intravenous SPEVIGO in Study Effisayil-1, ADAs formed with a median onset of 2.3 weeks. Following administration of 900 mg intravenous SPEVIGO, (12/50) 24% of subjects had a maximum ADA titer greater than 4000 and were neutralizing antibody (Nab)-positive by the end of the study (Weeks 12 to 17). In Study Effisayil-2, ADAs formed with a median onset of 8 weeks. Following administration of a 600 mg subcutaneous LD of SPEVIGO followed by 300 mg every 4 weeks for a total duration of 48 weeks, 24% of subjects had a maximum ADA titer greater than 4000 and were Nab-positive.
In Study Effisayil-1 following intravenous SPEVIGO, females appeared to have higher immunogenicity response; the percentage of subjects with ADA titer greater than 4000 was 30% in females, and 12% in males, respectively. In Study Effisayil-2 following administration of subcutaneous SPEVIGO, the data on immunogenicity response in males versus females were inconclusive.
10NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
10.1Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity and mutagenicity studies have not been conducted with spesolimab-sbzo.
No adverse effects on fertility were observed in male or female mice that were intravenously administered a surrogate antibody to IL36R at doses up to 50 mg/kg twice weekly.
11CLINICAL STUDIES
12HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
13PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
14INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SPEVIGO®(spea VEE go) (spesolimab-sbzo) injection, for subcutaneous use
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to inject SPEVIGO.
Read both sides of this Instructions for Use before you use SPEVIGO for the first time and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your or your child's medical condition or treatment. Your healthcare provider should show you or your child the right way to inject SPEVIGO before you try to inject yourself or your child for the first time. In children 12 to 17 years of age, SPEVIGO should be given under supervision of an adult.
SPEVIGO comes in a prefilled syringe with a safety cover.
SPEVIGO is for one-time use only. Do not reuse the prefilled syringes.
Your healthcare provider has prescribed a dose of SPEVIGO for you or your child that requires 2 injections (2 prefilled syringes) to deliver a complete dose. You must inject the contents of both SPEVIGO prefilled syringes that come in the carton to deliver the complete dose.
Getting to know SPEVIGO:
SPEVIGO comes in a prefilled syringe with a safety cover. The needle is pulled back into the safety cover after injection.
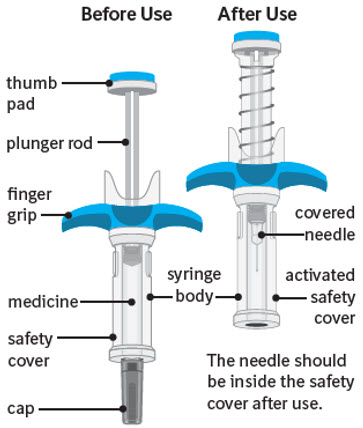
Guide to parts:
The figure below shows SPEVIGO before use, and after use with the activated safety cover.
Important information you need to know before injecting SPEVIGO:
- You must inject the contents of both SPEVIGO prefilled syringes to deliver a complete dose.
- Inspect the SPEVIGO carton to be sure that you have the correct medicine, 2 prefilled syringes for your or your child's prescribed dose, for any damage, and the expiration date.
- Do not use SPEVIGO if the liquid is cloudy or contains flakes or large or colored particles.
- Do not use SPEVIGO if the expiration date (EXP) has passed.
- Do not use SPEVIGO if the prefilled syringe has been dropped.
- Do not remove the cap until you are ready to inject.
- Inject SPEVIGO under the skin (subcutaneous injection) in either the upper thighs or stomach-area (abdomen). Do not inject SPEVIGO into any other area of the body.
Storing SPEVIGO:
Keep SPEVIGO and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Manufactured by:
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA
US License Number 2006
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA
US License Number 2006
Licensed from: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Ingelheim, Germany
SPEVIGO is a registered trademark of and used under license from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH.
SPEVIGO is a registered trademark of and used under license from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH.
Copyright © 2024 Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
COL12534AC152024
COL12534AC152024
For more information about SPEVIGO, including current prescribing information and Medication Guide, go to www.SPEVIGO.com, scan the code below, or call Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257.

This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Approved: 03/2024
Approved: 03/2024
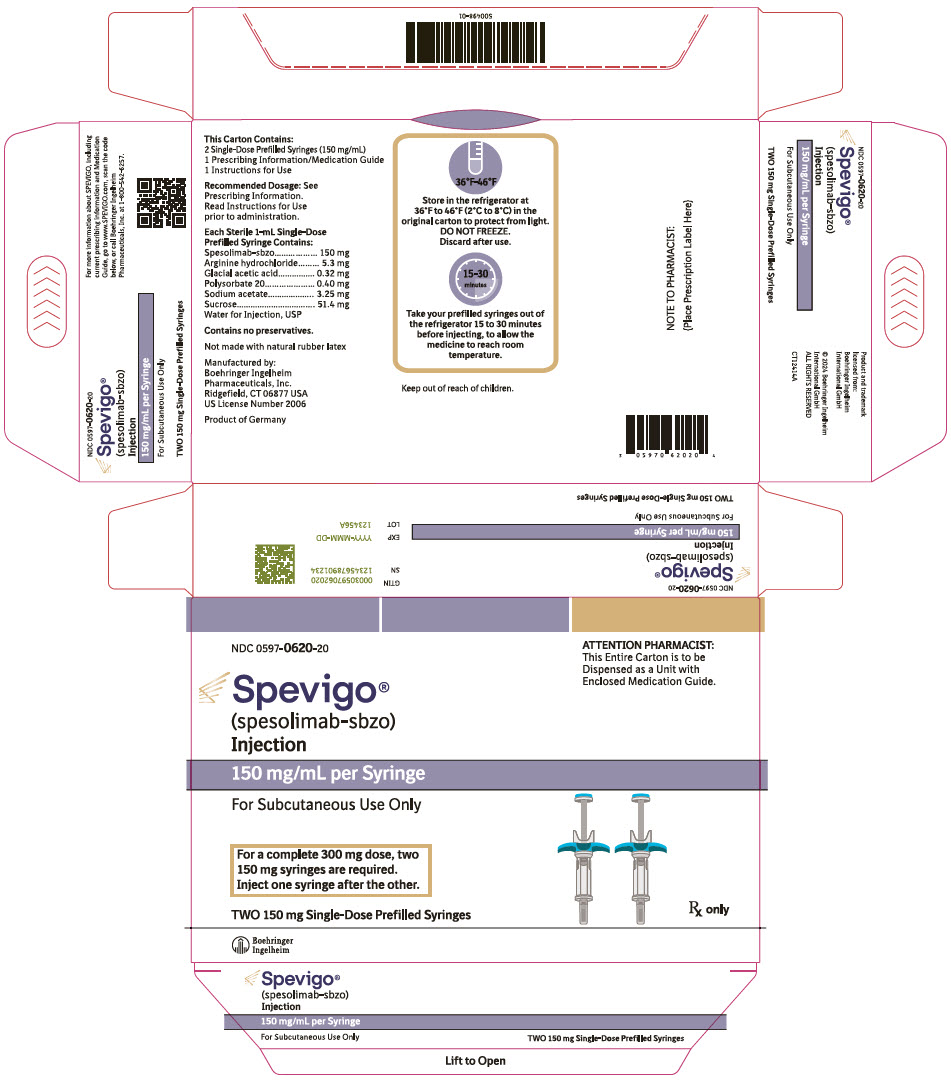
15PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 150 mg Syringe Carton
NDC 0597-0620-20
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
This Entire Carton is to be
Dispensed as a Unit with
Enclosed Medication Guide.
This Entire Carton is to be
Dispensed as a Unit with
Enclosed Medication Guide.
Spevigo®
(spesolimab-sbzo)
Injection
(spesolimab-sbzo)
Injection
150 mg/mL per Syringe
For Subcutaneous Use Only
For a complete 300 mg dose, two
150 mg syringes are required.
Inject one syringe after the other.
150 mg syringes are required.
Inject one syringe after the other.
TWO 150 mg Single-Dose Prefilled Syringes
Rx only
Boehringer
Ingelheim
Ingelheim
16PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 450 mg/7.5 mL Vial Carton
NDC 0597-0035-10
Rx only
Rx only
DISPENSE WITH ENCLOSED MEDICATION GUIDE
Spevigo®
(spesolimab-sbzo)
Injection
(spesolimab-sbzo)
Injection
450 mg/7.5 mL per vial
(60 mg/mL)
(60 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Infusion after Dilution
Discard Unused Portion
Discard Unused Portion
Prepare both vials in carton for
a complete dose of 900 mg
a complete dose of 900 mg
Contents: contains TWO - 450 mg/7.5 mL single-dose vials
Boehringer
Ingelheim
Ingelheim

Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Tired of the same old research?