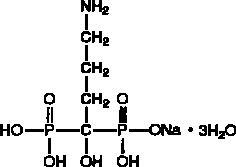
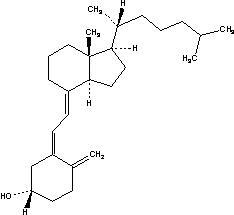
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
FOSAMAX
Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
FOSAMAX Daily
The safety of FOSAMAX in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis was assessed in four clinical trials that enrolled 7453 women aged 44-84 years. Study 1 and Study 2 were identically designed, three-year, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter studies (United States and Multinational; n=994); Study 3 was the three-year vertebral fracture cohort of the Fracture Intervention Trial [FIT] (n=2027); and Study 4 was the four-year clinical fracture cohort of FIT (n=4432). Overall, 3620 patients were exposed to placebo and 3432 patients exposed to FOSAMAX. Patients with pre-existing gastrointestinal disease and concomitant use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs were included in these clinical trials. In Study 1 and Study 2 all women received 500 mg elemental calcium as carbonate. In Study 3 and Study 4 all women with dietary calcium intake less than 1000 mg per day received 500 mg calcium and 250 international units Vitamin D per day.
Among patients treated with alendronate 10 mg or placebo in Study 1 and Study 2, and all patients in Study 3 and Study 4, the incidence of all-cause mortality was 1.8% in the placebo group and 1.8% in the FOSAMAX group. The incidence of serious adverse event was 30.7% in the placebo group and 30.9% in the FOSAMAX group. The percentage of patients who discontinued the study due to any clinical adverse event was 9.5% in the placebo group and 8.9% in the FOSAMAX group. Adverse reactions from these studies considered by the investigators as possibly, probably, or definitely drug related in greater than or equal to 1% of patients treated with either FOSAMAX or placebo are presented in Table 1.
Rash and erythema have occurred.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions: One patient treated with FOSAMAX (10 mg/day), who had a history of peptic ulcer disease and gastrectomy and who was taking concomitant aspirin, developed an anastomotic ulcer with mild hemorrhage, which was considered drug related. Aspirin and FOSAMAX were discontinued and the patient recovered. In the Study 1 and Study 2 populations, 49-54% had a history of gastrointestinal disorders at baseline, and 54-89% used nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or aspirin at some time during the studies. [See
Laboratory Test Findings: In double-blind, multicenter, controlled studies, asymptomatic, mild, and transient decreases in serum calcium and phosphate were observed in approximately 18% and 10%, respectively, of patients taking FOSAMAX versus approximately 12% and 3% of those taking placebo. However, the incidences of decreases in serum calcium to less than 8.0 mg/dL (2.0 mM) and serum phosphate to less than or equal to 2.0 mg/dL (0.65 mM) were similar in both treatment groups.
FOSAMAX Once-Weekly
The safety of FOSAMAX 70 mg once weekly for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis was assessed in a one-year, double-blind, multicenter study comparing FOSAMAX 70 mg once weekly and FOSAMAX 10 mg daily. The overall safety and tolerability profiles of once weekly FOSAMAX 70 mg and FOSAMAX 10 mg daily were similar. The adverse reactions considered by the investigators as possibly, probably, or definitely drug related in greater than or equal to 1% of patients in either treatment group are presented in Table 2.
Concomitant Use With Estrogen/Hormone Replacement Therapy
In two studies (of one and two years' duration) of postmenopausal osteoporotic women (total: n=853), the safety and tolerability profile of combined treatment with FOSAMAX 10 mg once daily and estrogen ± progestin (n=354) was consistent with those of the individual treatments.
Osteoporosis in Men
In two placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter studies in men (a two-year study of FOSAMAX 10 mg/day and a one-year study of once weekly FOSAMAX 70 mg) the rates of discontinuation of therapy due to any clinical adverse event were 2.7% for FOSAMAX 10 mg/day vs. 10.5% for placebo, and 6.4% for once weekly FOSAMAX 70 mg vs. 8.6% for placebo. The adverse reactions considered by the investigators as possibly, probably, or definitely drug related in greater than or equal to 2% of patients treated with either FOSAMAX or placebo are presented in Table 3.
FOSAMAX PLUS D
In a fifteen-week double-blind, multinational study in osteoporotic postmenopausal women (n=682) and men (n=35), the safety profile of FOSAMAX PLUS D (70 mg/2800 international units) was similar to that of FOSAMAX once weekly 70 mg. In the 24-week double-blind extension study in women (n=619) and men (n=33), the safety profile of FOSAMAX PLUS D (70 mg/2800 international units) administered with an additional 2800 international units vitamin D