Primaxin
What is Primaxin (Imipenem)?
Approved To Treat
Top Local Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of HRS-8427 in patients with complicated urinary tract infection, including acute pyelonephritis.
Summary: Mycobacterium abscessus (MABS) is a group of rapid-growing, multi-drug resistant non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) causing infections in humans. MABS pulmonary disease (MABS-PD) can result in significant morbidity, increased healthcare utilisation, accelerated lung function decline, impaired quality of life, more challenging lung transplantation, and increased mortality. While the overall numbers...
Summary: The primary purpose of this study is to assess the efficacy of oral TBP-PI-HBr as compared with intravenous (IV) imipenem-cilastatin with respect to the overall response (combined clinical cure plus microbiological eradication) at the Test-of-Cure (TOC) visit in hospitalized adult participants (≥18 years of age) with cUTI or AP.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- PRIMAXIN is not indicated in patients with meningitis because safety and efficacy have not been established.
- PRIMAXIN is not recommended in pediatric patients with CNS infections because of the risk of seizures [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
- PRIMAXIN is not recommended in pediatric patients less than 30 kg with impaired renal function, as no data are available [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4), and Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Periodic assessment of organ system functions, including renal, hepatic and hematopoietic, is advisable during prolonged therapy.
- The dosage of PRIMAXIN in adult patients should be based on suspected or confirmed pathogen susceptibility as shown in Table 1 below. The dosage recommendations for PRIMAXIN represent the quantity of imipenem to be administered. An equivalent amount of cilastatin is also present in the solution.
- These doses should be used for patients with creatinine clearance of greater than or equal to 90 mL/min. A reduction in dose must be made for patients with creatinine clearance less than 90 mL/min as shown in Table 3 [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Recommend that the maximum total daily dosage not exceed 4 g/day.
- Administer 500 mg by intravenous infusion over 20 to 30 minutes.
- Administer 1000 mg by intravenous infusion over 40 to 60 minutes.
- In patients who develop nausea during the infusion, the rate of infusion may be slowed.
- Do not mix PRIMAXIN with, or physically add to, other antibacterial drugs.
- PRIMAXIN may be administered concomitantly with other antibacterial drugs, such as aminoglycosides.
- 500 mg imipenem (anhydrous equivalent) and 500 mg cilastatin (free acid equivalent)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Seizure Potential [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Increased Seizure Potential Due to Interaction with Valproic Acid [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
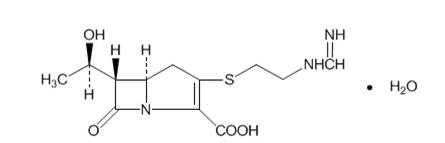
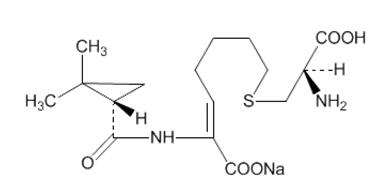
- Advise patients that allergic reactions, including serious allergic reactions, could occur and that serious reactions require immediate treatment. They should report any previous hypersensitivity reactions to PRIMAXIN, other carbapenems, beta-lactams or other allergens.
- Counsel patients that antibacterial drugs including PRIMAXIN should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When PRIMAXIN is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by PRIMAXIN or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
- Counsel patients to inform their physician:
- if they have central nervous system disorders such as stroke or history of seizures. Seizures have been reported during treatment with PRIMAXIN and with closely related antibacterial drugs.
- if they are taking valproic acid or sodium valproate. Valproic acid concentrations in the blood may drop below the therapeutic range upon co-administration with PRIMAXIN. If treatment with PRIMAXIN is necessary and continued, alternative or supplemental anti-convulsant medication to prevent and/or treat seizures may be needed.
- Advise patients that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs and usually resolves when the drug is discontinued. Sometimes, frequent watery or bloody diarrhea may occur and may be a sign of a more serious intestinal infection. If severe watery or bloody diarrhea develops, patients should contact their healthcare provider.
PRIMAXIN® I.V.
(IMIPENEM AND CILASTATIN FOR INJECTION)
CILASTATIN EQUIVALENT 250 mg
CAUTION: SINGLE DOSE VIAL / FOR I.V. USE ONLY
NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION
250 mg
MERCK & CO., INC., Whitehouse Station, NJ 08889, USA

PRIMAXIN® I.V.
(IMIPENEM AND CILASTATIN FOR INJECTION)
imipenem monohydrate), 500 mg cilastatin (equivalent to 531 mg
cilastatin sodium), and 20 mg sodium bicarbonate (used as a buffer).
NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION
500 mg
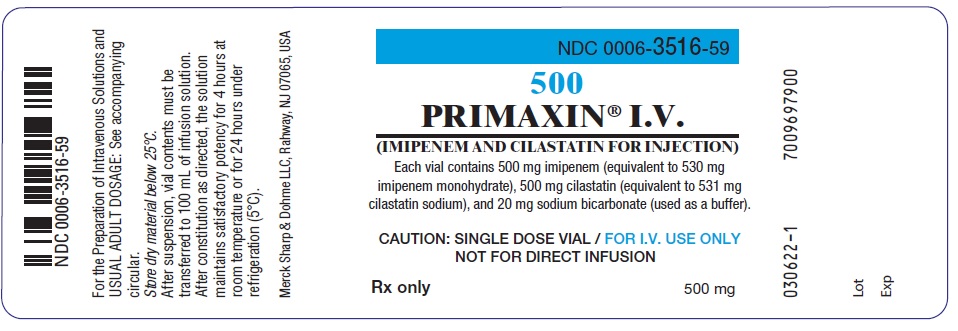
NDC 0006-3516-59
PRIMAXIN® I.V.
(IMIPENEM AND CILASTATIN FOR INJECTION)
(equivalent to 531 mg cilastatin sodium), and 20 mg sodium bicarbonate (used as a buffer).
CAUTION: SINGLE DOSE VIAL / FOR I.V. USE ONLY / NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION
For the Preparation of Intravenous Solutions and USUAL ADULT DOSAGE: See
accompanying circular. Color changes in solution from colorless to
yellow do not affect potency. Store dry material below 25ºC.
Rahway, NJ 07065, USA
Rahway, NJ, USA, and its affiliates.
All rights reserved.

CILASTATIN EQUIVALENT 250 mg
NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION
MERCK & CO., INC.
Whitehouse Station, NJ 08889, USA

CILASTATIN EQUIVALENT 500 mg
NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION
MERCK & CO., INC.
Whitehouse Station, NJ 08889, USA
