Brand Name
Lomaira
Generic Name
Phentermine
View Brand Information FDA approval date: July 01, 1976
Classification: Sympathomimetic Amine Anorectic
Form: Tablet, Capsule
What is Lomaira (Phentermine)?
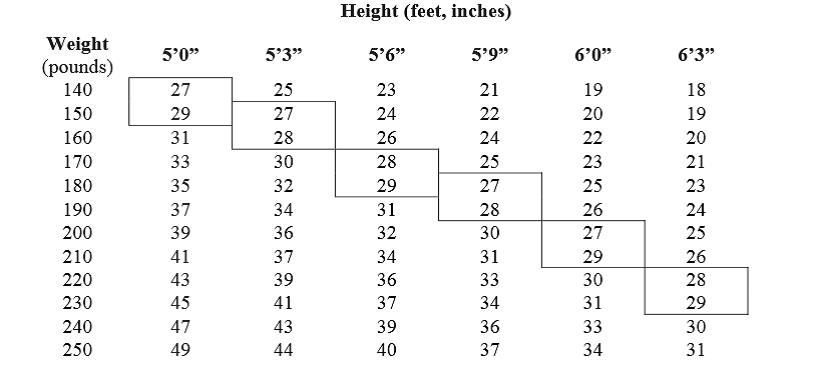
Phentermine hydrochloride, USP 15 mg and 30 mg is indicated as short-term adjunct in a regimen of weight reduction based on exercise, behavioral modification and caloric restriction in the management of exogenous obesity for patients with an initial body mass index greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2, or greater than or equal to 27 kg/m2 in the presence of other risk factors . Below is a chart of Body Mass Index based on various heights and weights. BMI is calculated by taking the patient’s weight, in kilograms , divided by the patient’s height, in meters , squared. Metric conversions are as follows: pounds.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
LOMAIRA (PHENTERMINE HYDROCHLORIDE)
1DESCRIPTION
Phentermine hydrochloride is a sympathomimetic amine anorectic. Its chemical name is α,α,-dimethylphenethylamine hydrochloride. The structural formula is as follows:
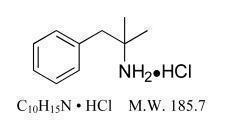
Phentermine hydrochloride is a white, odorless, hygroscopic, crystalline powder which is soluble in water and lower alcohols, slightly soluble in chloroform and insoluble in ether.
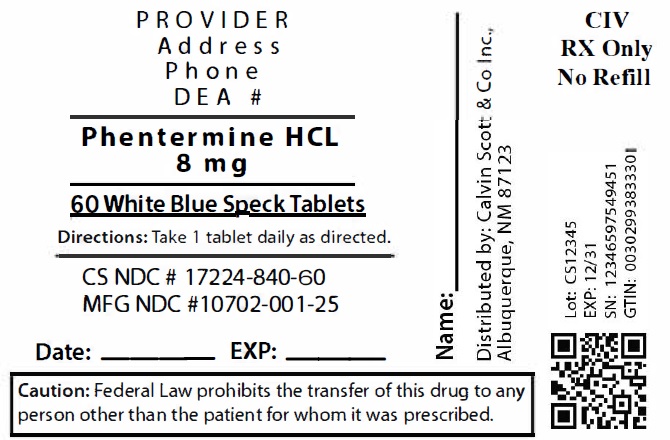
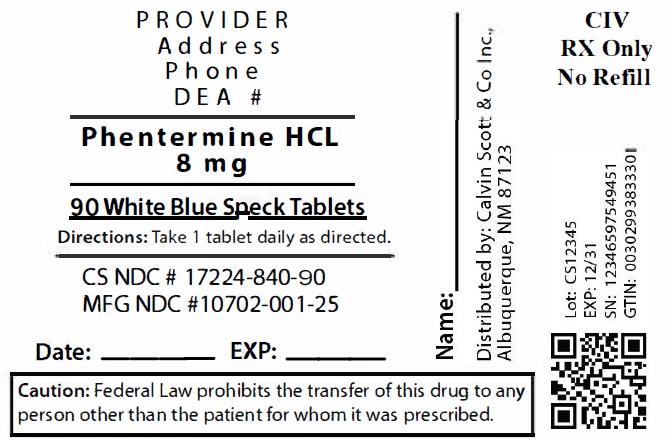
LOMAIRA™ tablet is available as an oral tablet containing 8 mg of phentermine hydrochloride (equivalent to 6.4 mg of phentermine base). Each LOMAIRA™ tablet also contains the following inactive ingredients: Corn Starch, Magnesium Stearate, NF, Microcrystalline Cellulose 102, NF, Stearic Acid, NF, FD&C Blue #1, Sucrose and Pharmaceutical Glaze.
2CLINICAL STUDIES
In relatively short-term clinical trials, adult obese subjects instructed in dietary management and treated with “anorectic” drugs lost more weight on the average than those treated with placebo and diet.
The magnitude of increased weight loss of drug-treated patients over placebo-treated patients is only a fraction of a pound a week. The rate of weight loss is greatest in the first weeks of therapy for both drug and placebo subjects and tends to decrease in succeeding weeks. The possible origins of the increased weight loss due to the various drug effects are not established. The amount of weight loss associated with the use of an “anorectic” drug varies from trial to trial, and the increased weight loss appears to be related in part to variables other than the drugs prescribed, such as the physician-investigator, the population treated and the diet prescribed. Studies do not permit conclusions as to the relative importance of the drug and non-drug factors on weight loss.
The natural history of obesity is measured over several years, whereas the studies cited are restricted to a few weeks’ duration; thus, the total impact of drug-induced weight loss over that of diet alone must be considered clinically limited.
3INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LOMAIRA™ tablets are indicated as a short-term (a few weeks) adjunct in a regimen of weight reduction based on exercise, behavioral modification and caloric restriction in the management of exogenous obesity in patients with an initial body mass index greater than or equal to 30 kg/m
Below is a chart of body mass index (BMI) based on various heights and weights.
BMI is calculated by taking the patient’s weight, in kilograms (kg), divided by the patient’s height, in meters (m), squared. Metric conversions are as follows: pounds ÷ 2.2 = kg; inches x 0.0254 = meters.
BODY MASS INDEX (BMI), kg/m
The limited usefulness of agents of this class, including phentermine (see
4CONTRAINDICATIONS
• History of cardiovascular disease (e.g., coronary artery disease, stroke, arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, uncontrolled hypertension)
5ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described, or described in greater detail, in other sections:
- Primary pulmonary hypertension (see
- Valvular heart disease (see
- Effect on the ability to engage in potentially hazardous tasks (see
- Withdrawal effects following prolonged high dosage administration (see
The following adverse reactions to phentermine have been identified:
5.1Cardiovascular
Primary pulmonary hypertension and/or regurgitant cardiac valvular disease, palpitation, tachycardia, elevation of blood pressure, ischemic events.
5.2Central Nervous System
Overstimulation, restlessness, dizziness, insomnia, euphoria, dysphoria, tremor, headache, psychosis.
5.3Gastrointestinal
Dryness of the mouth, unpleasant taste, diarrhea, constipation, other gastrointestinal disturbances.
5.4Allergic
Urticaria.
5.5Endocrine
Impotence, changes in libido.
6OVERDOSAGE
The least amount feasible should be prescribed or dispensed at one time in order to minimize the possibility of overdosage.
6.1Acute Overdosage
Manifestations of acute overdosage include restlessness, tremor, hyperreflexia, rapid respiration, confusion, assaultiveness, hallucinations, and panic states. Fatigue and depression usually follow the central stimulation. Cardiovascular effects include arrhythmia, hypertension or hypotension, and circulatory collapse. Gastrointestinal symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal cramps. Overdosage of pharmacologically similar compounds has resulted in fatal poisoning usually terminates in convulsions and coma.
Management of acute phentermine hydrochloride intoxication is largely symptomatic and includes lavage and sedation with a barbiturate. Experience with hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis is inadequate to permit recommendations in this regard. Acidification of the urine increases phentermine excretion. Intravenous phentolamine (Regitine
6.2Chronic Intoxication
Manifestations of chronic intoxication with anorectic drugs include severe dermatoses, marked insomnia, irritability, hyperactivity and personality changes. The most severe manifestation of chronic intoxications is psychosis, often clinically indistinguishable from schizophrenia. See
7DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosage should be individualized to obtain an adequate response with the lowest effective dose.
Late evening medication should be avoided because of the possibility of resulting insomnia.
8HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
LOMAIRA™ is available as follows:
LOMAIRA™ 8 mg is supplied as white butterfly shaped tablets with blue speckles, debossed “K1” on one side and bisected on the other side.
Bottles of 30, NDC 10702-001-03
Bottles of 60, NDC 10702-001-06
Bottles of 90, NDC 10702-001-09
Bottles of 250, NDC 10702-001-25
Bottles of 500, NDC 10702-001-50
Bottles of 1000, NDC 10702-001-10
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure (as required).
Keep out of the reach of children.
Manufactured by:
Item ID# 006178/07
Manufacturer’s Code: 10702 09/16
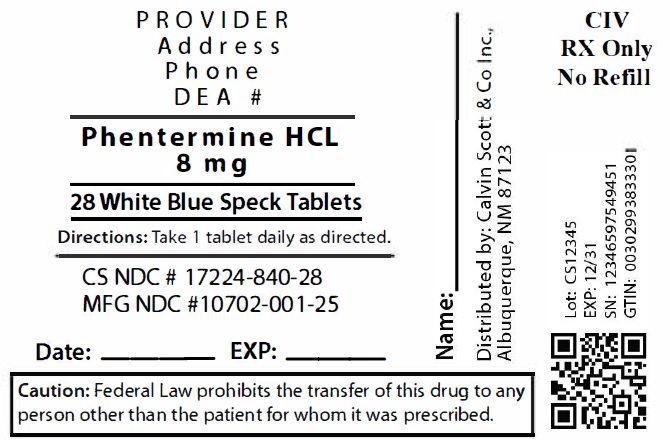
9Package Labeling:17224-840-28
10Package Labeling:17224-840-60
11Package Labeling:17224-840-90
12Package Labeling:17224-840-30
